Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Doctors in Eugene, OR
Is a laparoscopic hysterectomy right for you? Laparoscopic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgical technique in which a camera and tiny incisions are used to remove the uterus. Compared to open surgery, this method usually causes less discomfort, a faster recovery, and less scarring. It is frequently done to treat diseases like cancer, uterine fibroids, and irregular bleeding. Dr. Richard Beyerlein MD, CPI, FACOG and Tamara A. Stenshoel, MD, FACOG offer laparoscopic hysterectomy at Pacific Women’s Center. For more information, contact us or schedule an appointment online. We are located at 911 Country Club Rd. Suite 222, Eugene, OR 97401.
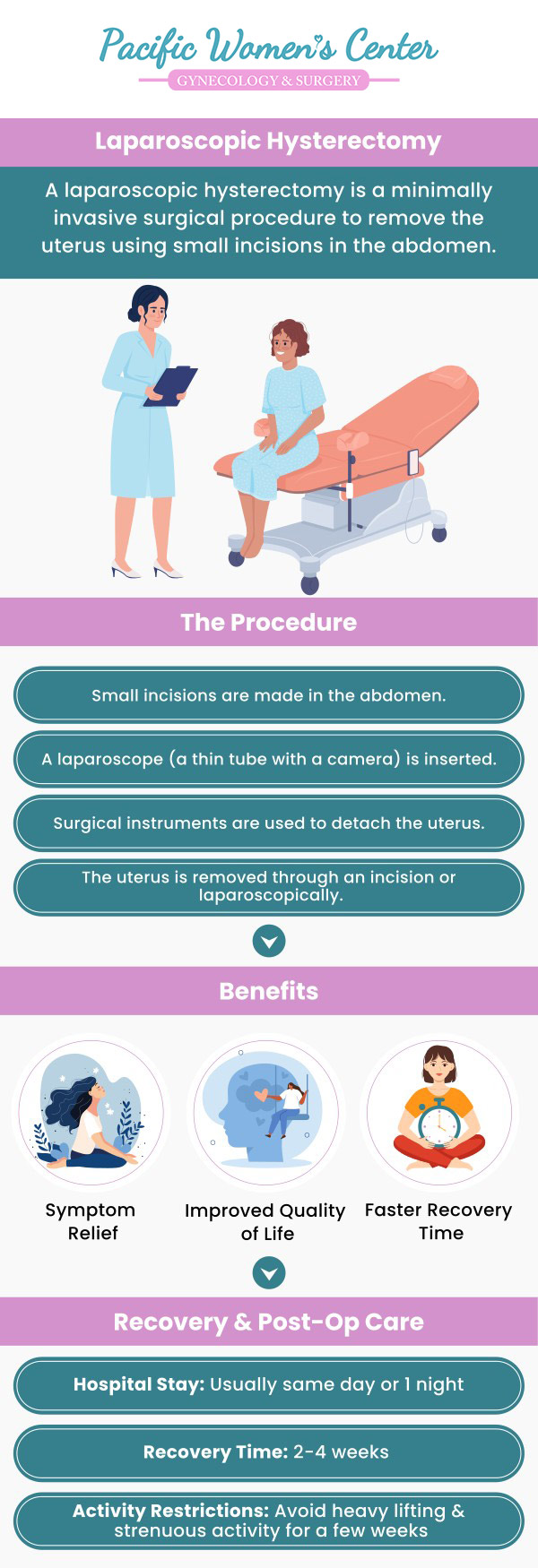
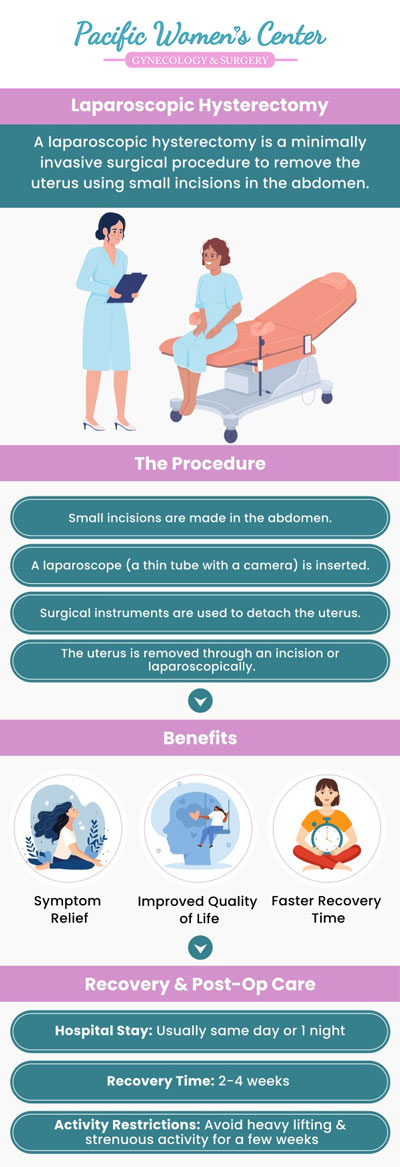


Table of Contents:
How long does it take to recover from a laparoscopic hysterectomy?
Why is a Laparoscopic hysterectomy performed?
What is a laparoscopic hysterectomy?
Who should have laparoscopic hysterectomy surgery?
During a laparoscopic hysterectomy, the uterus is removed. The uterus is removed through small cuts in your belly using a lighted tube and surgical tools. A laparoscopic hysterectomy requires fewer incisions than an abdominal hysterectomy which means it has a faster recovery time and causes less discomfort and pain.
Each day, you can expect to feel stronger and better. Mild shoulder and back pain are also normal. This is the result of gas that has been injected into your belly to help your doctor see your organs more clearly. You may have less energy or feel tired more easily than usual. Fatigue may persist for several days following the surgery. There is likely to be swelling and puffiness around your belly. A full recovery may take about one to two weeks.
In order to heal properly, you should avoid lifting heavy objects while you recover. Other steps patients can take to recover include resting when fatigue sets in, engaging in light physical activities such as walking, and consulting their physician if they are considering being sexually active following their procedure.
An abdominal hysterectomy can be replaced with a laparoscopic hysterectomy, which is a minimally invasive procedure. Laparoscopic hysterectomy appears to be less painful, less invasive, and less risky than abdominal hysterectomy. Patients who have laparoscopic hysterectomy return to work and normal activities more quickly.
In laparoscopic hysterectomy, a thin, flexible tube containing a video camera is used to perform a vaginal hysterectomy. A tiny incision near the navel is used to insert thin tubes. Utilizing a laparoscope tube or a vaginal approach, the uterus is then removed in sections.
Hysterectomies are generally performed to treat fibroids, abnormal uterine bleeding, and prolapse of the pelvic organs, which are not cancerous. Depending on your condition, your healthcare provider will determine which type of hysterectomy you need. The procedure will determine whether it is necessary to remove the fallopian tubes and/or ovaries.
The uterus and cervix of a woman who undergoes a total hysterectomy are removed, but the ovaries remain in place. A supracervical hysterectomy involves removing only the upper part of the uterus and leaving the cervix intact. During a total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, the cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries are removed. In women who have not experienced menopause, removing the ovaries will trigger symptoms of menopause.
Radical hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy involves removing the ovaries, uterus, cervix, upper portion of the vagina, fallopian tubes, and some surrounding tissue and lymph nodes. When cancer is present, this type of hysterectomy is performed.
During a hysterectomy, the uterus and most likely the cervix are removed surgically. Surrounding organs like the fallopian tubes and ovaries may be removed as part of a hysterectomy, depending on the reason for the surgery. During pregnancy, the uterus is the place where the baby grows. Blood shed during a menstrual cycle makes up the lining of the uterus. A hysterectomy prevents you from getting pregnant and prevents you from getting your period.
In contrast to a traditional abdominal hysterectomy that requires a 3–6-inch incision, a laparoscopic hysterectomy requires only a few small incisions. Consequently, there is less blood loss, scarring, and post-operative pain. While an abdominal hysterectomy typically requires a 2–3-day hospital stay, a laparoscopic hysterectomy usually requires an outpatient procedure. After a laparoscopic procedure, the recovery period is 1-2 weeks, compared to 4-6 weeks after an abdominal hysterectomy.
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is less likely to cause blood loss and infection than abdominal hysterectomy. It takes about as long as an abdominal hysterectomy to complete a laparoscopic hysterectomy if the procedure is performed by an experienced surgeon.
In most cases, a laparoscopic hysterectomy can be performed to treat abnormal uterine bleeding or fibroids. In some cases, it may not be possible. The procedure is not typically performed for women with gynecologic cancer.
Previous operations in the lower abdomen may also suggest laparoscopic hysterectomy surgery is not the best choice. For more information, contact us or schedule an appointment online. We are located at 911 Country Club Rd. Suite 222, Eugene, OR 97401. We serve patients from Eugene OR, Cottage Grove OR, Coburg OR, Lowell OR, Creswell OR, Springfield OR, and Junction City OR.

ADDITIONAL SERVICES YOU MAY NEED
❱ Abdominal Hysterectomy
❱ Bladder Lift Surgeon Q&A
❱ Cervical Cone Biopsy
❱ Colposcopy
❱ Endometrial Ablation
❱ Endometrial Biopsy
❱ Female Sexual Dysfunction
❱ Gynecological Surgery
❱ Gynecology
❱ Hormone Therapy
❱ Vaginal Hysterectomy
❱ Endometriosis Diagnosis & Care