Colposcopy Specialist in Eugene OR
Colposcopy – Dr. Richard Beyerlein MD
Colposcopy is a procedure that examines the vagina, cervix, and vulva to look for signs of cancer. Colposcopy is required when an abnormal pap smear test, an abnormal pelvic exam, and positive HPV test results are found. Colposcopy techniques are used to diagnose bleeding, polyps, DES exposure, acute pelvic inflammatory disorders, and acute cervix inflammation. Colposcopy is a quick and painless technique offered by Dr. Richard Beyerlein MD, CPI, FACOG, and Tamara A. Stenshoel, MD, FACOG to assess cancer risk and potential outcomes. For more information, contact us or schedule an appointment online. We are located at 911 Country Club Rd. Suite 222, Eugene, OR 97401.
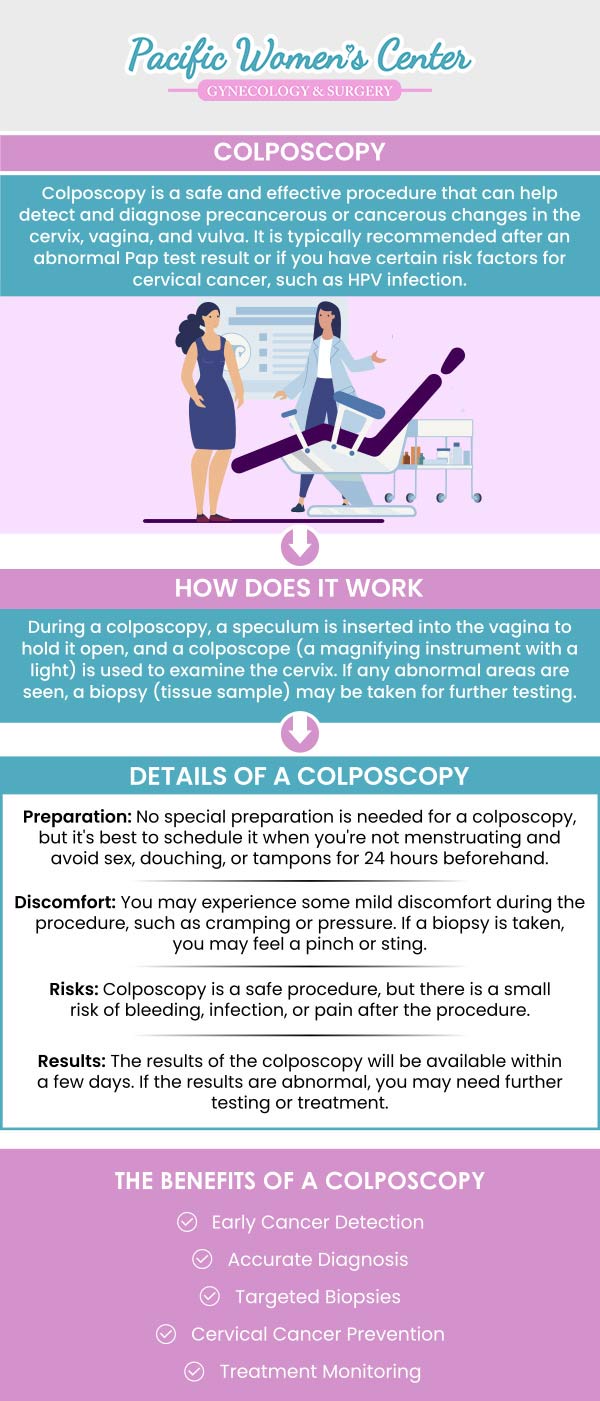
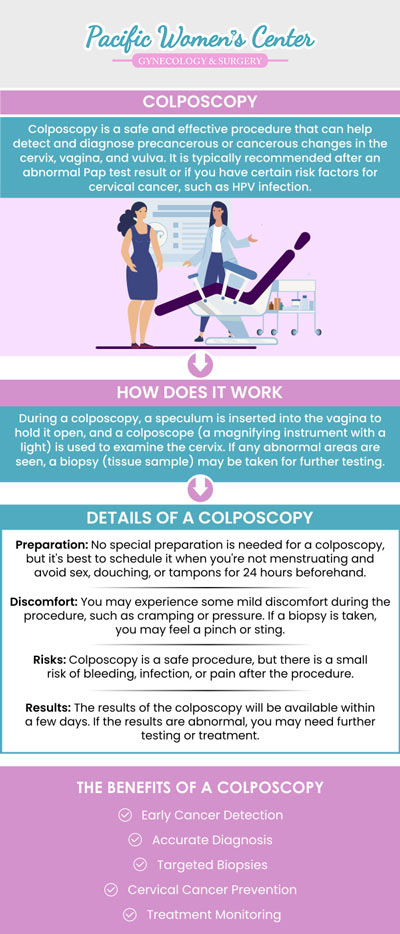
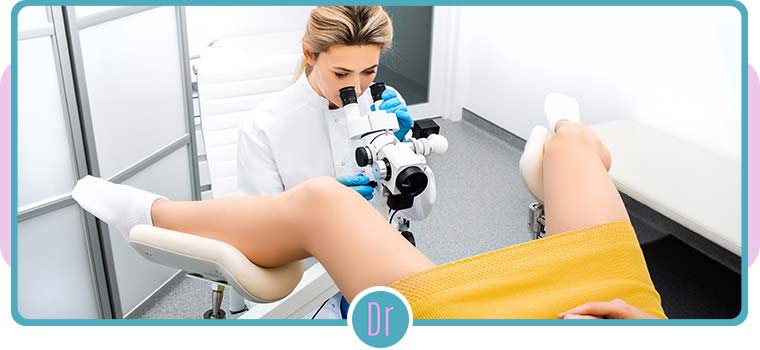
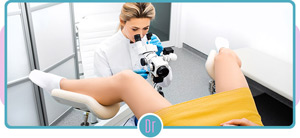
Table of Contents:
What is the procedure for Colposcopy?
What happens during a Colposcopy?
What does a colposcopy test for?
Should I be worried if I need a colposcopy?
Colposcopy is a procedure used to examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva for abnormal cells or precancerous growths. During the procedure, a colposcope, which is a microscope with a light attached, is used to magnify the area being examined. The procedure is performed by a gynecologist or a colposcopist, in a clinic setting. Colposcopy is a safe and quick procedure. It usually takes around 10 to 20 minutes to perform a colposcopy.
The procedure begins with the patient being positioned on an exam table in the lithotomy position, with their feet in stirrups. A speculum, which is a metal or plastic medical device, is inserted into the vagina to hold it open, and the cervix is then visualized with the colposcope. The cervix is typically swabbed with a solution to help highlight any abnormal areas. The doctor will then examine the cervix for any abnormal cells or growths, and may take a sample of tissue from any suspicious areas, which is known as a biopsy.
During the colposcopy procedure, the doctor may also perform other diagnostic tests such as an endocervical curettage (ECC) which is a scraping of the endocervical canal. An ECC is done to help diagnose abnormal cells that may not be visible on the surface of the cervix.
After the biopsy and other diagnostic tests, the procedure is typically over, and the patient can return to normal activities. There may be some mild cramping or light bleeding after the procedure. The biopsy samples will be sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results will be sent to the doctor who will then discuss the results with the patient and develop a treatment plan.
A colposcopy test is typically performed when abnormal results are found on a cervical cancer screening test, such as a Pap smear. A Pap smear is used to detect cervical dysplasia, which is abnormal growth of cervical cells, or cervical cancer.
The colposcopy test can also be used to locate the source of abnormal vaginal bleeding or to identify other abnormal cervical or vaginal conditions. A colposcopy can be used to diagnose a variety of cervical and vaginal conditions including:
Cervical dysplasia – An abnormal growth of cervical cells, which can be precancerous or cancerous, is known as cervical dysplasia.
Cancer – An abnormal growth of cells that invades surrounding tissue and can spread to other parts of the body is known as cancer. A colposcopy can detect cervical, vaginal and culver cancers.
Vaginal or cervical infections – Common vaginal or cervical infections include Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, chlamydia and gonorrhea.
Benign cervical or vaginal growths – Common non-cancerous growths include cervical or vaginal polyps.
Abnormal vaginal bleeding – To find the cause of heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding, a colposcopy can be performed.
Other cervical or vaginal conditions – Other conditions that can be detected by a colposcopy include ectropion, a condition in which the cervical cells are present on the outer surface of the cervix, and cervical or vaginal warts.
It is normal to feel a bit anxious or worried if your healthcare provider recommends a colposcopy. However, it is important to remember that the test is typically performed when abnormal results are found on a cervical cancer screening test, such as a Pap smear. Having abnormal results on a screening test does not mean that you have cancer, but it does mean that further testing is needed to determine if there are any abnormal cervical or vaginal cells that need to be treated.
If abnormal cells are found during the colposcopy, your healthcare provider will discuss the next steps with you, which may include a biopsy or other follow-up tests. In most cases, abnormal cervical or vaginal cells can be successfully treated and do not progress to cancer.
For more information, contact us or schedule an appointment online. We are located at 911 Country Club Rd. Suite 222,, Eugene, OR 97401. We serve patients from Eugene OR, Springfield OR, Coburg OR, Lowell OR, Creswell OR, Cottage Grove OR, Junction City OR, and surrounding areas.

ADDITIONAL SERVICES YOU MAY NEED
❱ Abdominal Hysterectomy
❱ Bladder Lift Surgeon Q&A
❱ Cervical Cone Biopsy
❱ Colposcopy
❱ Endometrial Ablation
❱ Endometrial Biopsy
❱ Female Sexual Dysfunction
❱ Gynecological Surgery
❱ Gynecology
❱ Hormone Therapy
❱ Vaginal Hysterectomy
❱ Endometriosis Diagnosis & Care