Why Confidential STD Testing Is Essential for Your Well-Being
Confidential STD testing is essential for early detection, treatment, and protecting your overall health and privacy. Dr. Richard Beyerlein MD, CPI, FACOG, and Tamara A. Stenshoel, MD, FACOG at Pacific Women’s Center in Eugene, OR, provide discreet, expert care for your peace of mind. For more information, contact us or schedule an appointment online. We are conveniently located at 911 Country Club Rd. Suite 222, Eugene, OR 97401.
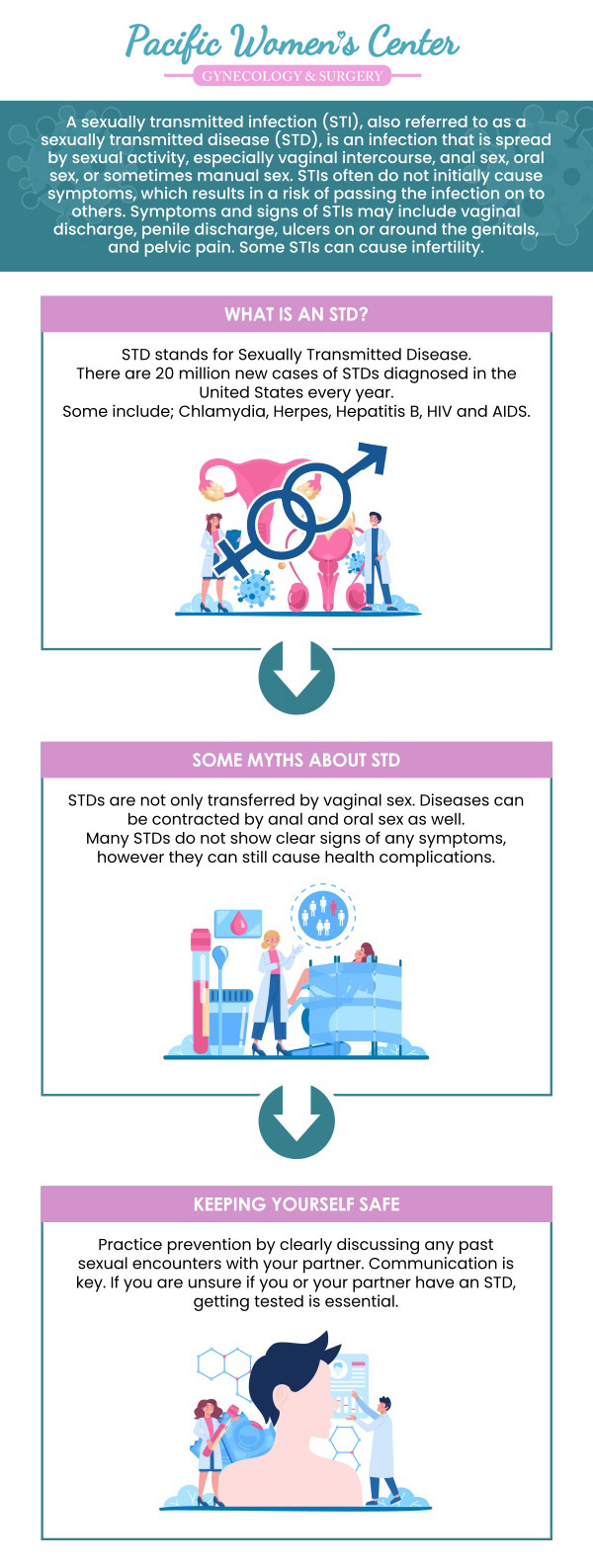
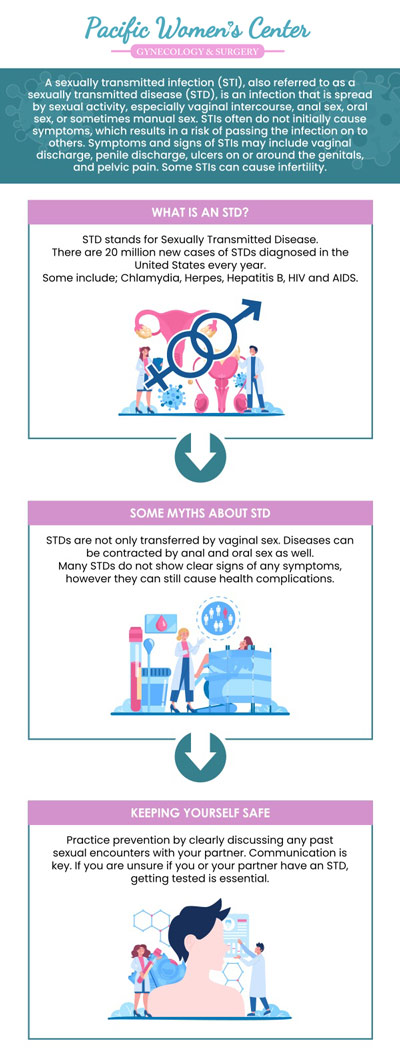


Table of Contents:
What is an STD screening test?
What STDs can be detected by Pap smears?
Do normal blood tests show STDs?
How soon can you test for STDs?
Although regular STD testing is recommended for any sexually active person, it is normal to feel some anxiety about doing so. At Pacific Women’s Center, our medical professionals are committed to providing a safe place for you to receive confidential STD testing, as well as any treatment or management of an STD.
An STD screening test is a medical procedure that assesses whether a patient has a sexually transmitted disease or infection (STD or STI). STD screening tests can be performed using either a blood draw, a urine sample, or a swab. In some cases, a positive diagnosis for an STD can be arrived at with a visual inspection for things such as genital warts or pubic lice.
Blood tests are used to test for STDs such as hepatitis B and C (hepB and hepC), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and syphilis. Less often, blood tests can also be used to test for the herpes simplex virus (HSV). During such tests, the medical professional or clinician will take a small vial of blood, most likely from your arm, using a small needle. The blood sample will then be sent to a medical laboratory for testing. You will be notified as soon as your results come back, which could take between seven to ten days.
Swab tests can detect such STDs as chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, human papillomavirus (HPV), and trichomoniasis. During swab tests, your medical provider will likely use a long swab that is similar to a Q-tip to take a sample of fluid from your anus, throat, or vagina, depending on which area of the body is most likely to contain the STD. You can expect results to return from swab tests within a week, upon which you will be notified.
Urine tests can also detect chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis. In general, urine tests are far more pleasant than swab tests, as they only require that you pee into a collection cup or tube. The results are then sent to a laboratory, which should come back within one week.
During a Pap smear, your doctor can also collect samples of fluid from the cervix to test for human papillomavirus. The primary purpose of a Pap smear is to examine your cervix for cell changes that could progress into cervical cancer. However, since cell changes are often caused by the human papillomavirus, Pap smears can also detect whether an individual has HPV. Pap smears are unable to test for any other sexually transmitted disease or infection accurately.
A normal blood test is typically a complete blood count (CBC), which can indicate the possible presence of a sexually transmitted disease or infection based on the patient’s white or red blood cell level. That said, the tests used to detect various STDs are typically more specific to the STD that is being tested, such as the hepatitis virus panel, the rapid plasma regain (RPR) test for syphilis and other tests.
The recommended time to get tested for sexually transmitted diseases or infections varies according to the incubation period for each STD or STI, which are listed as follows:
• Chlamydia: seven to 21 days
• Genital or oral herpes: two to 12 days
• Gonorrhea: one to 14 days
• Hepatitis A: 15 to 50 days
• Hepatitis B: eight to 22 weeks
• Hepatitis C: two to 26 weeks
• Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): two to four weeks
• Human papillomavirus (HPV): one month to ten years
• Syphilis: three weeks to 20 years, depending on whether it is latent or not
• Trichomoniasis: five to 28 days
For more information, contact us today. Or, when ready, you can book in online to schedule an appointment at your earliest convenience. We are conveniently located at 911 Country Club Rd. Suite 222, Eugene, OR 97401. We serve patients from Eugene OR, Springfield OR, Coburg OR, Creswell OR, Cottage Grove OR, Lowell OR, Junction City OR, and surrounding areas.

ADDITIONAL SERVICES YOU MAY NEED
❱ Abdominal Hysterectomy
❱ Bladder Lift Surgeon Q&A
❱ Cervical Cone Biopsy
❱ Colposcopy
❱ Endometrial Ablation
❱ Endometrial Biopsy
❱ Female Sexual Dysfunction
❱ Gynecological Surgery
❱ Gynecology
❱ Hormone Therapy
❱ Vaginal Hysterectomy
❱ Endometriosis Diagnosis & Care